A typical long bone consists of the following parts :-
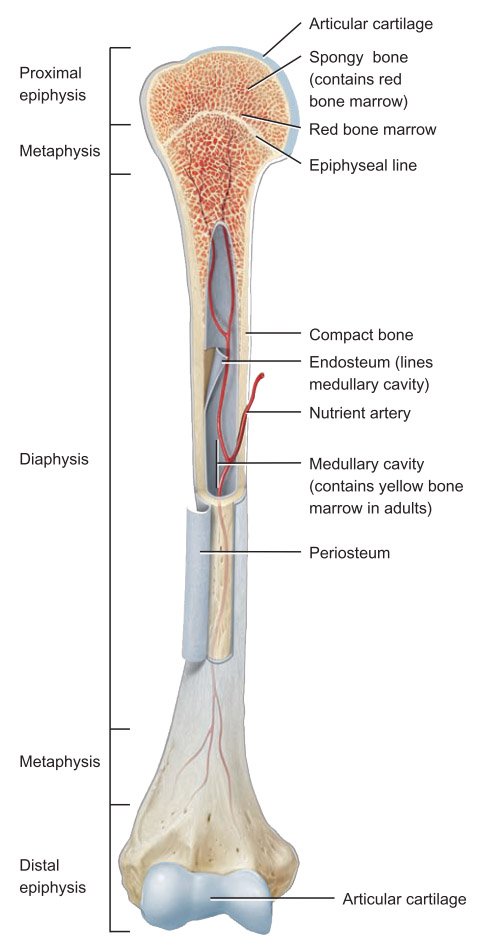
1. The diaphysis :- (growing between) is the bone’s shaft, or body—the long, cylindrical, main portion of the bone.
2. The epiphyses :- (growing own; singular is epiphysis) or extremities are the proximal and distal ends of the bone.
3. The metaphyses :- (between; singular is metaphysis) are the regions between the diaphysis and the epiphyses.
• In a growing bone, each metaphysis contains an epiphyseal (growth) plate (ep-i-FIZ-e–al), a layer of hyaline cartilage that allows the diaphysis of the bone to grow in length.
• When bone growth in length stops somewhere between the ages of 18 and 21, the cartilage in the epiphyseal plate is replaced by bone and the resulting bony structure is known as the epiphyseal line.
4. The articular cartilage :- It is a thin layer of hyaline cartilage covering the part of the epiphysis where the bone forms an articulation (joint) with another bone.
• Articular cartilage reduces friction and absorbs shock at freely movable joints. Because articular cartilage lacks a perichondrium and lacks blood vessels, repair of damage is limited.
5. The periosteum :- (peri-⫽around) It is a tough connective tissue sheath and its associated blood supply that surrounds the bone surface wherever it is not covered by articular cartilage.
• It is composed of an outer fibrous layer of dense irregular connective tissue and an inner osteogenic layer that consists of cells. Some of the cells enable bone to grow in thickness, but not in length.
• The periosteum also protects the bone, assists in fracture repair, helps nourish bone tissue, and serves as an attachment point for ligaments and tendons.
• The periosteum is attached to the underlying bone by perforating (Sharpey’s) fibers, thick bundles of collagen that extend from the periosteum into the bone extracellular matrix.
6. The medullary cavity :- (medulla-⫽marrow, pith), or marrow cavity, It is a hollow, cylindrical space within the diaphysis that contains fatty yellow bone marrow and numerous blood vessels in adults.
•This cavity minimizes the weight of the bone by reducing the dense bony material where it is least needed. The long bones’ tubular design provides maximum strength with minimum weight.
7. The endosteum :-(endo-⫽within) It is a thin membrane that lines the medullary cavity. It contains a single layer of bone-forming cells and a small amount of connective tissue.